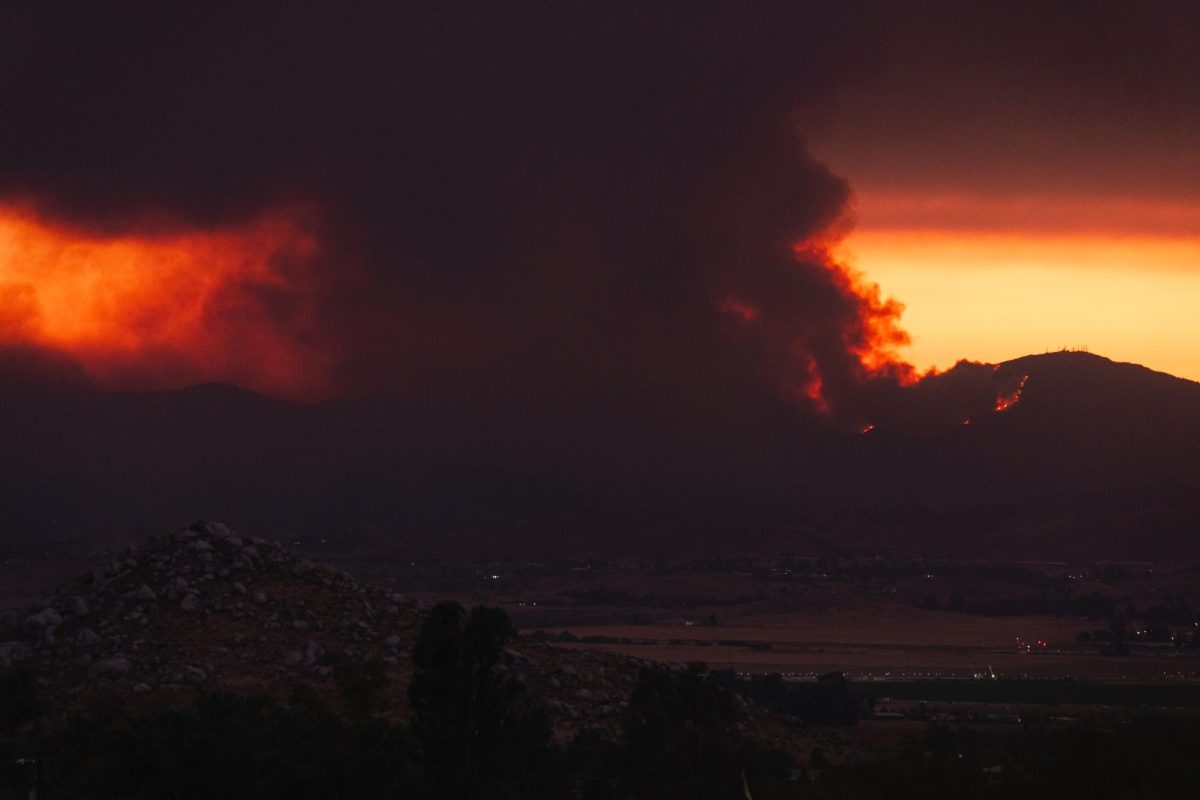
The recent years of weird weather patterns in each season have worsened and raised confusion in many people’s minds about the temperature and weather patterns, affecting the environment in many places. The recent heat waves in Southern California caused by climate change set the records in both September and October. These patterns get worse each season; summer 2024 did not have as many heat waves as Autumn 2024. The LA Times mentioned that international climate officials have declared that summer 2024 was Earth’s hottest on record. The season has sparked explosive wildfires, sizzling heat waves for weeks, etc, in California and many parts of the world.

Many people question how heat waves affect the environment and why we should care. Firstly, the air quality during heat waves is associated with air stagnation, which can lead to significant deterioration of air quality. It can worsen the air quality and significantly impact human health, the environment, and climate change by increasing harmful air pollution. The mortality risk from extreme heat and air pollutants exposure is significantly greater than from exposure to either factor alone. Heat waves can occur with other hazards, such as droughts, dust storms, pollution events, or wildfires. Heat waves can lead to water shortages and reduced plant growth, which is the basis of the food chain. It can also create hot and dry conditions favorable to the start and spread of forest fires, affecting the animals in the environment. Heat waves are becoming more common and severe as climate change warms the planet.
With climate change and animals in the habitats, climate change exacerbates other threats like habitat destruction, overexploitation of wildlife, and disease. From the shrinking habitat of the polar bear to increased water scarcity driving human-wildlife conflict, these changes will become more pronounced in years to come. It causes animals to move into different habitats by altering their preferred temperature ranges, forcing them to seek cooler areas by migrating to higher elevations or latitudes. This also made them search for suitable environments to survive and access food sources adapting to the changing climate.

Excessive heat can also damage crops, reduce crop yields, quality, and production, and increase the risk of heat stress in livestock, leading to lower milk production, slower growth, and reduced fertility. Additionally, extreme temperatures during food storage and transport can lead to food losses, shortened shelf life, and waste. As for the farmers themselves, it can impact their health due to heat-related illnesses and kidney diseases. In the recent NPR article, “California farmers turn to agave amid drought conditions and climate change,” Secaria mentioned that “experts say droughts will likely persist and even intensify with climate change. When drought strikes, water gets affected. And in California, farmers have struggled to keep crops like almonds, which require a lot of water, healthy.”
Raising awareness about climate change is essential as it can affect many aspects of life, including health, the environment, and the economy. Climate change is damaging the environment by threatening rainforests and other habitats. It also causes species to move into new areas or change their migration patterns. It also threatens the economy by making it harder to grow food and increasing the cost of living. It is also more important as climate change can be a major health threat by causing air pollution, disease, and mental health pressures. It can also lead to more frequent and intense weather events like storms, floods, droughts, and wildfires.
References
Secaira Manola. (2024, September 9) “California farmers turn to agave amid drought conditions and climate change.”
NPR. npr.org.
Smith Hayley. (2024, September 6) “As California swelters, climate officials declare Summer 2024 the hottest on record.”
Los Angeles Times. latimes.com.
https://www.latimes.com/environment/story/2024-09-06/summer-2024-was-earths-hottest-on-record
(2023, October 12) “Climate Change.” World Health Organization. who.int.