4-H, a renowned youth development program, has empowered young people across the United States for over a century. While its roots lie in agriculture, 4-H has evolved to encompass a wide range of interests and skills, making it a valuable resource for youth in Southern California and beyond. However, despite its rich history and impact, 4-H is facing a decline in membership in Southern California, raising concerns about its future in the region.
4-H stands for Head, Heart, Hands, and Health, representing the four values that guide its programs. Established in 1902, 4-H aims to provide young people with hands-on learning experiences in agriculture, STEM, leadership, and life skills, preparing them to be responsible, engaged members of society.
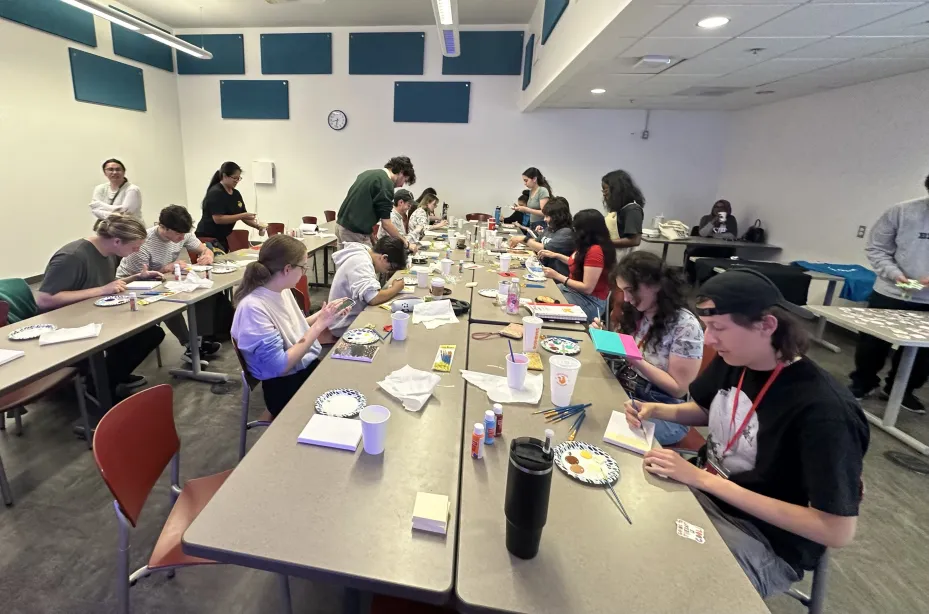
In Southern California, 4-H offers a variety of programs and activities tailored to the unique interests and needs of youth in the region. From urban gardening to robotics, 4-H clubs in Southern California allow young people to explore their passions, develop new skills, and connect with peers who share their interests.
“4-H is more than just a youth organization—it’s a community that fosters growth, learning, and friendship,” says Phillip Flores, a 4-H parent in Southern California. “My children have benefited greatly from their involvement in 4-H, gaining confidence, leadership skills, and a deeper appreciation for the world around them.
Despite its many benefits, 4-H faces challenges in Southern California that impact its membership numbers. One key challenge is the perception of 4-H as primarily focused on rural activities. While 4-H has its roots in agriculture, it offers various programs beyond farming and animal husbandry, including STEM, leadership, and civic engagement. However, many families in urban and suburban areas need to be made aware of these diverse opportunities, leading to lower community participation rates.
A local 4-H member expressed their concern: “When I asked people in my community about 4-H, many of them said they had never heard of it.” This sentiment highlights a common challenge faced by 4-H in Southern California: a lack of awareness about the program and its benefits among the general public. Despite California’s significant population size, totaling over 39 million residents, the state only boasts 46,631 youth members in 4-H programs. In stark contrast, Nebraska, with a population of just under 2 million, has over 110,000 youth members enrolled in 4-H.
Despite these challenges, efforts are underway to address the decline in 4-H membership in Southern California. Local 4-H chapters are implementing outreach programs in schools and communities to raise awareness about the benefits of 4-H participation. These efforts include interactive workshops, hands-on activities, and partnerships with local farms and businesses to provide experiential learning opportunities.
As 4-H continues to evolve, it remains committed to its core values of empowering youth and building a better future for all. Through its programs and activities, 4-H strives to instill a sense of responsibility, leadership, and service, in young people, preparing them to be the next generation of leaders and innovators.
“4-H is more than just a program—it’s a philosophy,” says Jessica Ramirez, a 4-H leader in Southern California. “It’s about empowering young people to make a positive difference in the world, both now and in the future.”